Increasingly, we are seeing new business models being developed to hold, manage, and process data by implementing technologies such as Machine Learning, Blockchain, and Artificial Intelligence. With ever more data and the roll-out of smart meters, the “Internet of Energy” is slowly becoming a reality, increasing the need for data management even further.
In 2017, Cryptocurrencies fuelled interest in Blockchain technology, with many start-ups and pilot projects being funded by Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs), which seemed to be being launched on an almost daily basis! In the energy sector alone, there were over 150 projects using Blockchain, according to SolarPlaza, which it highlighted in a ‘Comprehensive Guide of Companies involved in Blockchain & Energy’.
If you look at Google Trends to see the interest in terms of searches since December 2017, “Blockchain Energy” has fallen from 100 to 26, so clearly, the hype has gone. However, we are still seeing a number of projects in the energy sector being developed in different parts of the world.
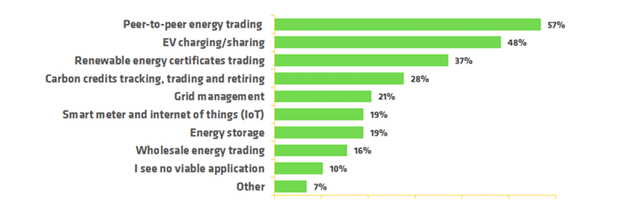
In France, Grenoble Ecole de Management conducted a survey to ask 112 experts from industry, science, and public administration in France about the role of Blockchain technology in the French energy sector. It wanted to understand how these experts thought Blockchain would be used in the next five years. Peer-to-peer energy trading and electric vehicle charging and sharing were the most popular choices.
Digisol, based in France, is a project designed with an objective to enable the sharing of solar energy between two apartments within the same building.
Meanwhile, in Japan, an Australian company has been using Blockchain technology to enable solar initiatives and working to expand the renewable energy market in Japan. Perth-based Power Ledger has announced a partnership with Japan’s Sharing Energy Company. Power Ledger is providing a Blockchain-based tokenised energy trading platform while Sharing Energy is a provider of solar installations and equipment.
According to Solar Market Insight, the USA installed 2.7 gigawatts (GW) of solar PV capacity in the first quarter of 2019. This brings the total amount of solar power installed capacity to 67 GW, which is enough to power 12.7 million homes. Furthermore, it is estimated that PV installations will double in the next five years, which will assist in reducing the impact of power generation on climate change. However, it presents some real challenges for power management and the electricity grid in the USA. In California, for example, solar farms have previously had to shut down on sunny days because the grid in the state was unable to handle the amount of solar energy being generated.
In 2012, Germany experienced industrial companies sustaining damages due to the instability of its electricity grid due to unprecedented solar and wind fluctuations. In Australia, there were major state-wide blackouts in 2016 for the same reasons.
This week a company called LO3 successfully gained funding from Royal Dutch Shell and Japanese giant Sumitomo Corporation Group. LO3 is looking at using Blockchain technology to track energy supplies, allowing users to select which supplier they wish to select so making peer-to-peer...
Increasingly, we are seeing new business models being developed to hold, manage, and process data by implementing technologies such as Machine Learning, Blockchain, and Artificial Intelligence. With ever more data and the roll-out of smart meters, the “Internet of Energy” is slowly becoming a reality, increasing the need for data management even further.
In 2017, Cryptocurrencies fuelled interest in Blockchain technology, with many start-ups and pilot projects being funded by Initial Coin Offerings (ICOs), which seemed to be being launched on an almost daily basis! In the energy sector alone, there were over 150 projects using Blockchain, according to SolarPlaza, which it highlighted in a ‘Comprehensive Guide of Companies involved in Blockchain & Energy’.
If you look at Google Trends to see the interest in terms of searches since December 2017, “Blockchain Energy” has fallen from 100 to 26, so clearly, the hype has gone. However, we are still seeing a number of projects in the energy sector being developed in different parts of the world.
In France, Grenoble Ecole de Management conducted a survey to ask 112 experts from industry, science, and public administration in France about the role of Blockchain technology in the French energy sector. It wanted to understand how these experts thought Blockchain would be used in the next five years. Peer-to-peer energy trading and electric vehicle charging and sharing were the most popular choices.
Digisol, based in France, is a project designed with an objective to enable the sharing of solar energy between two apartments within the same building.
Meanwhile, in Japan, an Australian company has been using Blockchain technology to enable solar initiatives and working to expand the renewable energy market in Japan. Perth-based Power Ledger has announced a partnership with Japan’s Sharing Energy Company. Power Ledger is providing a Blockchain-based tokenised energy trading platform while Sharing Energy is a provider of solar installations and equipment.
According to Solar Market Insight, the USA installed 2.7 gigawatts (GW) of solar PV capacity in the first quarter of 2019. This brings the total amount of solar power installed capacity to 67 GW, which is enough to power 12.7 million homes. Furthermore, it is estimated that PV installations will double in the next five years, which will assist in reducing the impact of power generation on climate change. However, it presents some real challenges for power management and the electricity grid in the USA. In California, for example, solar farms have previously had to shut down on sunny days because the grid in the state was unable to handle the amount of solar energy being generated.
In 2012, Germany experienced industrial companies sustaining damages due to the instability of its electricity grid due to unprecedented solar and wind fluctuations. In Australia, there were major state-wide blackouts in 2016 for the same reasons.
This week a company called LO3 successfully gained funding from Royal Dutch Shell and Japanese giant Sumitomo Corporation Group. LO3 is looking at using Blockchain technology to track energy supplies, allowing users to select which supplier they wish to select so making peer-to-peer energy much easier. LO3 Energy Blockchain-powered platform was used in Brooklyn in New York in 2017 and was the world’s first peer-to-peer electricity trading project, developed with Siemens.
Blockchain technology is helping power grids become more decentralised, so accommodating microgeneration and peer-to-peer power supplies. By using Blockchain technology buyers, sellers and transmitters of energy can be sure of the privacy and security of the transactions (also reducing the number of intermediaries), so improving electricity market efficiency. In addition to this, the use of Smart Contracts enables the automation of records and payments, by potentially using Digital currencies.
 Repsol, the Spanish energy company, has recently invested in FinBoot, which is a business with offices in London and Barcelona.
Repsol, the Spanish energy company, has recently invested in FinBoot, which is a business with offices in London and Barcelona.